Immunotherapy shows spectacular success in treating cancers, but unfortunately only in a minority of patients. A study by the Gstaiger (IMSB), Aebersold (IMSB), and Malissen group (CIML CNRS, Inserm, AMU Marseille), which appeared in Cell Reports, identifies using proteomics and mouse models molecular mechanisms that might account for some of the failures observed during immunotherapy.
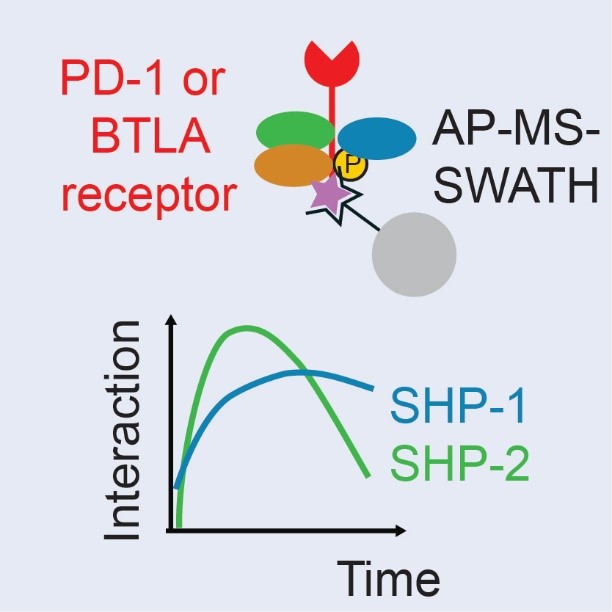
The PD-1 and BTLA inhibitory receptors expressed on the surface of anti-tumor T cells use two tyrosyl phosphatases (SHP-1 and SHP-2) to block the destruction of tumor cells. The concomitant inhibition of PD-1 and BTLA should allow to increase the efficiency of certain immunotherapies.
Copyright: Bernard Malissen/CIML
Immunotherapy is the newest pillar in cancer therapy. Cancer cells can trick the immune system and suppress immune responses against them by expressing a ligand on their surface that activates inhibitory receptors (such as PD-1) on T cells. Blocking this interaction with new immunotherapy drugs led to spectacular therapy successes, but only in a subset of patients. In the published study, the Malissen (CIML CNRS, Inserm, AMU Marseille), Gstaiger and Aebersold (IMSB, ETH Zurich) laboratories used engineered mouse models and sensitive mass spectrometry-based proteomics to identify the mode of action of the PD-1 and BTLA inhibitory receptors in T cells. They discovered that these two inhibitory receptors can use either of two tyrosyl-phosphatases (SHP-1 and SHP-2), and that these phosphatases can substitute for each other to enable PD-1 signaling. These findings provide a mechanistic rationale for concomitant inhibition of PD-1 and BTLA to increase the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Sources
Quantitative Interactomics in Primary T Cells Provides a Rationale for Concomitant PD-1 and BTLA Coinhibitor Blockade in Cancer Immunotherapy
Celis-Gutierrez J, Blattmann P, Zhai Y, Jarmuzynski N, Ruminski K, Grégoire C, Ounoughene Y, Fiore F, Aebersold R, Roncagalli R, Gstaiger M, Malissen B. Cell Rep., 2019 , 27(11):3315-3330.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.05.041, PMID: 31189114
Contact
Bernard Malissen
Centre d'immunologie de Marseille-Luminy
Email : here