Florent GINHOUX - Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, FRA
Host : Eric VIVIER
RÉJANE RUA HIGHLIGHTED BY LA PROVENCE AND FRANCE 3: THE CIML RESEARCHER REVOLUTIONIZES ALZHEIMER'S AND AUTISM RESEARCH.
Following the article published in La Provence on Wednesday, August 6, 2025, the work of Réjane Rua, team leader at the Center for Immunology of Marseille Luminy (CIML) Inserm, CNRS, AMU, is gaining increasing media recognition. The researcher is being honored on France 3 Provence Alpes Côte d'Azur this Tuesday, August 12, for her discoveries on the interactions between the immune system and the brain.
Réjane Rua's research has demonstrated the crucial role of macrophages present in the meninges. These immune cells not only constitute the first line of defense against infections, but also participate in memory and behavioral processes by contributing to the formation and activation of neurons.
This 38-year-old researcher was selected as a "Rising Star" by the International Union of Immunological Societies in 2023 (IUIS), joined the European EMBO Young Investigator program in 2024, and received a prestigious grant from the European Research Council (ERC).
These discoveries open promising avenues for the development of new treatments against neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's, Parkinson's), neurodevelopmental disorders (autism), and certain psychiatric pathologies (schizophrenia). Her international team of nine researchers conducts in-depth studies to understand communication between the meninges and brain, with the objective of bringing new momentum to the study of these pathologies.

CNRS Bronze Medal recognizes Achille Broggi, team leader at CIML, for his research on innate immunity
The CNRS researcher at the Centre d'Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy is awarded for his work on interferons and epithelial tissue regeneration.
Achille Broggi is the recipient of the 2025 CNRS Bronze Medal. This distinction honors his remarkable contributions to the study of innate immunity mechanisms, particularly his discoveries on the complex role of interferons in tissue protection and repair.
His research focuses on type I interferons and their influence on intestinal epithelial balance in contexts of chronic inflammation and infection. The scientist is particularly interested in understanding why the organism has multiple interferon systems that appear to have similar functions.
After studying translational medicine in Milan, Achille Broggi joined Harvard Medical School for his postdoctoral training. There, he studied interferon lambda (IFN-λ), an antiviral molecule distinguished by its localized action, primarily at the mucosal level. This specificity guided his research toward understanding this targeted immune system.
The researcher demonstrated that IFN-λ plays a modulatory role by protecting mucosae through calming neutrophil responses. However, his work revealed a paradox: during prolonged respiratory infections, this antiviral interferon can hinder tissue repair and promote secondary infections by preventing epithelial cell regeneration. This counter-intuitive discovery shows that an antiviral interferon can become detrimental in certain viral infections depending on the kinetics of the immune response.
Established at CIML where he now leads his research team, he has extended his investigations to the digestive system. His research on chronic inflammatory bowel diseases has shown that IFN-λ disrupts mucosal regeneration by activating a specific sensory receptor in cells responsible for tissue repair. This activation leads these cells toward cell death, a mechanism observed both in experimental models and in patients.
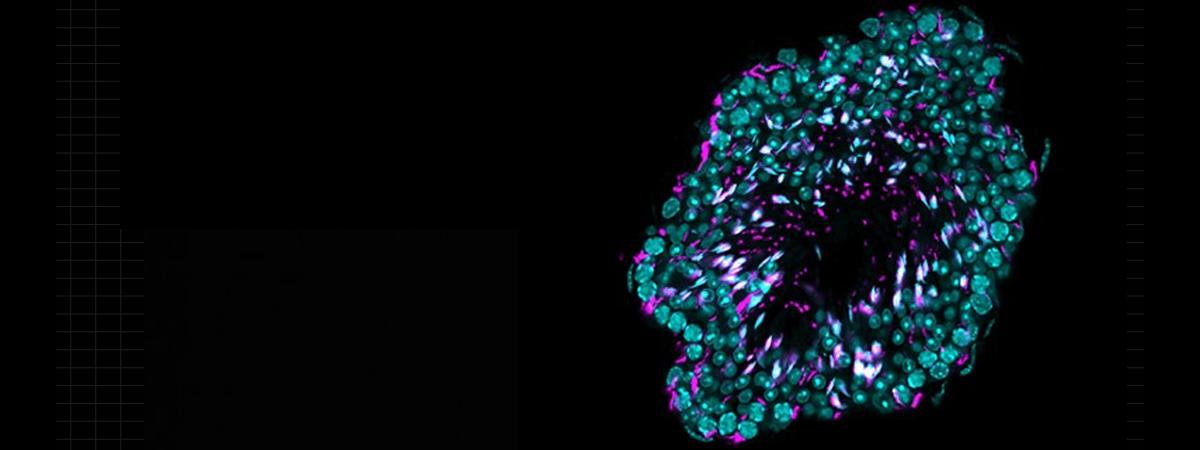
The use of organoids has allowed the scientist to bridge controlled animal models and clinical reality. This innovative technology has opened the way for him to establish direct links between his experimental observations and potential therapeutic applications in humans.
Achille Broggi develops his research with a translational perspective, establishing collaborations with Marseille's Hôpital Nord and the national REMIND group. This approach allows him to integrate clinical data to refine his experimental models and develop new therapeutic avenues.
This distinction reflects the scientific excellence of the Centre d'Immunologie de Marseille-Luminy, which brings together more than 200 scientists working on fundamental immunity mechanisms. The CNRS Bronze Medal annually recognizes the promising early work of about forty young researchers.

https://www.provence-corse.cnrs.fr/fr/personne/achille-broggi
Events
News
At the crossroads of biology and medicine, immunology is a scientific discipline that focuses on the operating mechanisms of the immune system. Appeared early in the evolution, this system enables living organisms to defend themselves against pathogens or their own components when they are altered. It involves a large number of cells whose capacity for cooperation, recognition and memory are far from having revealed all their secrets.
Publications
CIML ERC GRANTS
ERC "Advanced Grants"
Bernard Malissen – 2018 – Basilic Projet
Michael Sieweke – 2016 – Macrophage Aging and Rejuvenation
Eric Vivier – 2016 – Targeting Innate Lymphoid Cells
Bernard Malissen – 2012 – Integrative biology of T cells and dendritic cells in vivo
Eric Vivier – 2010 – The Immune Function of Natural Killer
ERC "Consolidator Grants"
Sophie Ugolini – 2014 – Neural regulation of immunity
Marc Bajénoff – 2014 – Immunobiology of lymphoid stromal cells
ERC "Starting Grants"
Mauro Gaya - 2022 - Outlining the role of IgA in Memory Instruction
Réjane Rua - 2020 - Spatiotemporal control of neuroinfection by meningeal macrophages
Marc Dalod – 2011 – Harnessing systems immunology to unravel dendritic cell subset biology
Toby Lawrence - 2010 – Targeting tumor associated macrophages in Cancer
ERC "Proof of Concept (PoC) Grant"
Eric Vivier - 2019 - MInfla-TilcERC
ERC "Synergy Grant"
Eric Vivier - 2023 - Immunotherapy of liver metastases
Vidéos
Discover our close-ups and our video archives.